There’s a good chance a butterfly needle was used the last time you had blood drawn or were given IV medication. 23 gauge butterfly needles are one of the most popular sizes. It may not seem important, but it is very important for the patient’s safety and correct blood collection. The purpose of this guide is to explain what a 23 gauge butterfly needle is, how it works, when it is used, and why healthcare professionals choose it.
What Is a Butterfly Needle?
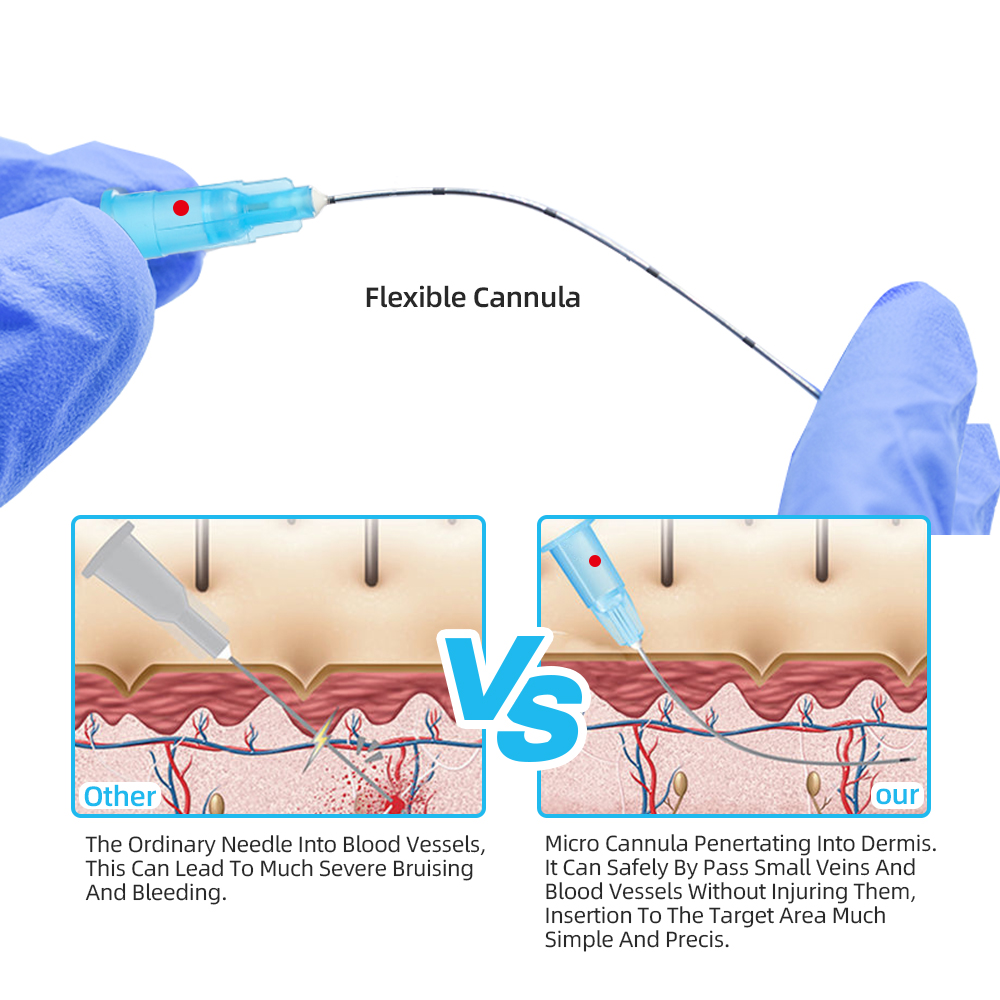
A butterfly needle is a small needle with two flexible plastic “wings” on each side. These wings help healthcare workers hold the needle steady during blood draws or IV access.
Butterfly needles are also called:
- Winged infusion sets
- Winged needles
- Butterfly IV needles
They are designed for short-term use and are often used when veins are small, fragile, or hard to find.
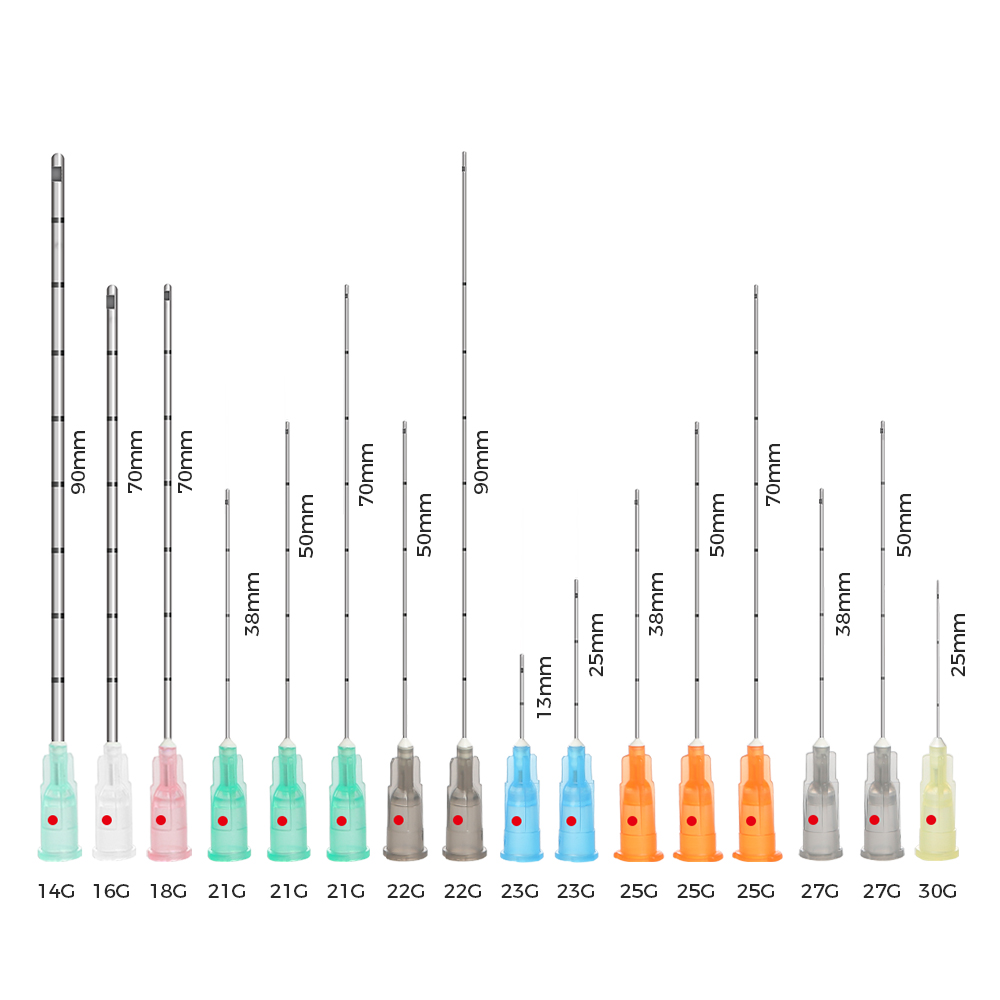
What Does “23 Gauge” Mean?
The word gauge refers to the thickness of the needle.
Understanding Needle Gauge Size
- When the gauge number goes up, the needle gets smaller.
- When the gauge number goes down, the needle gets larger.
That means a 23 gauge butterfly needles is a bit smaller than a 21 gauge needle but not quite as thick as a 25 gauge needle.
Why Gauge Size Matters
What the gauge does is:
- Level of comfort
- Blood flow speed
- Vein safety
- accurate lab results
People often choose a butterfly needle 23 gauge size because it is a good compromise between being able to place the needle gently and reliable blood flow.
What Is a 23 Gauge Butterfly Needle?
A 23 gauge butterfly needles is a thin, winged needle attached to flexible tubing. It is commonly used for blood draws and short IV treatments, especially in patients with delicate veins.
Important Things About a 23 Gauge Butterfly Needles
- Thin needle (23 gauge)
- Short needle length
- soft plastic wings for control
- Flexible Tubing
- A safety shield included
Hospitals, clinics, labs, and outpatient centers all allow this type of needle.
Parts of 23 gauge Butterfly Needle
Getting to know the parts can help you figure out why it works so well.
Needle
- The thin stainless steel
- Sharp Beveled Tip
- Designed for Smooth Insertion
Wings
- Soft, flexible plastic
- Handle and grip better.
- Can be taped down to keep it stable
Tubing
- Easy to use and flexible
- It’s easy to connect to IV lines or collection tubes.
Safety Mechanism
To prevent needlestick injuries, the majority of modern 23 gauge butterfly needles have a safety shield that locks over the needle after use.
Common Uses of a 23 Gauge Butterfly Needle
Healthcare providers choose a 23 gauge butterfly needles for various reasons. It works well when comfort and precision matter.
Blood Draws (Venipuncture)
Drawing blood for lab tests is a common use. The thin needle minimizes discomfort and maintains proper blood flow.
Pediatric Patients
Children often have smaller veins. A 23 gauge butterfly needles helps reduce pain and lowers the chance of vein damage.
Older Patients
As people age, veins can become fragile. This needle size helps prevent vein collapse and bruising.
Patients With Difficult Veins
Patients who are:
- Dehydrated
- Undergoing chemotherapy
- Very thin
- Chronically ill
often benefit from a 23 gauge butterfly needles.
Why Healthcare Professionals Choose a 23 Gauge Butterfly Needle
More Control During Insertion
The wings help the doctor keep the needle stable and put it in at a shallow angle. This makes things more accurate and comfortable.
Less anxiety for patients
The smaller size appears less scary than the bigger needles. This may help patients feel less anxious during operations.
Less Chance of Damaging Veins
The slim design makes it less likely that:
- Vein collapse
- The bruising process
- Infiltration
Blood Tests That Are Reliable
A 23 gauge butterfly needles enables for effective blood collection for most basic lab procedures while being thin.
23 Gauge Butterfly Needle vs Other Needle Sizes
Butterfly Needle: 23 Gauge vs. 21 Gauge
21 gauge: Adults with strong veins should use a 21 gauge needle for faster, thicker blood flow.
23 gauge: It’s thinner, softer, and better for veins that are small or weak.
Butterfly Needle: 23 Gauge vs. 25 Gauge
25 Gauge: Very thin and slow blood flow
23 gauge: A little thicker and has a better mix of ease and flow.
A lot of labs like 23 gauge because it is patient-friendly and lowers the risk of hemolysis.
Is a 23 Gauge Butterfly Needle Painful?
The amount of pain varies on a lot of things, like how skilled the person is who is placing the needle and how healthy the veins are in the patient.
Why it hurts less most of the time
- A thinner needle does less damage to tissue.
- Short needles can’t move around as much inside the vein.
- The wings help keep the pen steady.
A best 23 gauge butterfly needles is often described by patients as feeling more like a quick pinch than as sharp pain.
How Long Can a 23 Gauge Butterfly Needle Stay in Place?
A butterfly needle is meant for short-term use only.
Typical Time Limits
- Blood draw: removed immediately after collection
- IV access: usually no more than a few hours
It is not designed for long-term IV therapy.
Safety and Infection Control
Single use only
A 23 gauge butterfly needles is always single use. It is dangerous and against the law in hospital situations to reuse needles.
Sterile Packaging
To prevent contamination, each needle is sealed.
Safe Disposal
To protect healthcare workers and patients, the needle is put into a sharps container after use.
Advantages and Disadvantage Using a 23 Gauge Butterfly Needle
Advantages
- Gentle on veins
- Easier to control
- Ideal for small or fragile veins
- Reduces patient stress
- Widely available
Disadvantage
- It is useful, but not ideal for all scenarios.
- Reduced Blood Flow
- A thinner size may reduce blood collection speed compared to larger gauges.
- Not Suitable for Every Test
- Tests needing large blood volumes may require a thicker needle.
Who Should Avoid Using a 23 Gauge Butterfly Needle?
For patients with large, strong veins requiring quick blood collection, a lower gauge needle can be more effective. Healthcare providers select needle size according to the situation.
Why Patients Often Prefer Butterfly Needles
Many patients say butterfly needles feel:
- Less scary
- More comfortable
- Faster and smoother
This preference is one reason they are widely used in labs and clinics.
Final Thoughts: Is a 23 Gauge Butterfly Needle Right for You?
A 23 gauge butterfly needles is a small but powerful tool in modern healthcare. It offers comfort, precision, and safety for patients who need gentle vein access. From blood tests to short IV treatments, it plays a key role in everyday medical care.
If you are nervous about needles or have been told you have small veins, this type of needle may be exactly what your healthcare provider chooses—and for good reason.
Understanding what it is and how it works can make your next blood draw feel a little less stressful and a lot more manageable.
 +86-791-8686-1216
+86-791-8686-1216