Phlebotomy tubes are very important in medical care. It is important to know what blood collection tubes are for and how they work, whether you work in a hospital, a clinical lab, or as a student learning the ropes. This guide talks about everything, from picking the right tube for a test to buying good stuff online.
We’ll dive into everything from the types of phlebotomy tubes and their color-coded system to proper usage, common errors when using blood collection tubes, and tips for buying phlebotomy blood collection tubes online for both clinical use and inventory planning.
What Are Phlebotomy Tubes?
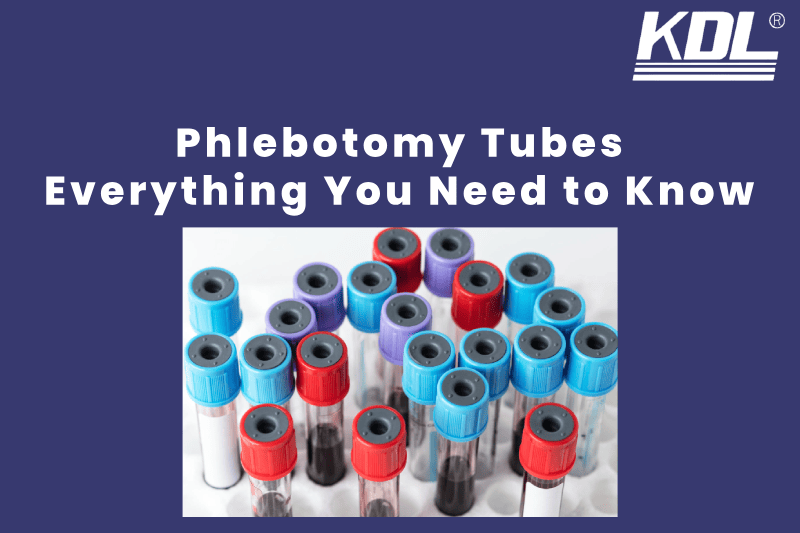
Phlebotomy tube, also known as blood collection tubes or vacutainers, are sterile, vacuum – sealed tubes used to collect blood samples for laboratory testing. These tubes come in various colors, each indicating a different additive or want thereof, which preserves or prepares the blood sample for specific tests however
Understanding which phlebotomy tube to use is crucial for accurate diagnosis and efficient lab work, especially when using phlebotomy blood tubes for hospitals and clinics.
The Phlebotomy Tubes Color-Coded System: What Do the Tube Colors Mean?
Each tube’s cap color indicates the type of additive inside the tube, which determines what kind of test the blood can be used for. Here’s a quick look at some of the most common tubes:

1. Red Top Tubes
- Additive: None or clot activator
- Used For: Serum testing, blood chemistry
- Popular Choice For: Red top blood collection tubes for chemistry tests and phlebotomy tubes with clot activator for serum testing
2. Blue Top Tubes
- Additive: Sodium citrate
- Used For: Coagulation tests
- Best Fit: Phlebotomy tubes for coagulation testing with sodium citrate
3. Green Top Tubes
- Additive: Heparin
- Used For: Plasma testing
4. Lavender or Purple Top Tubes
- Additive: EDTA
- Used For: Hematology, complete blood counts (CBC)
- Perfect When You Need: Phlebotomy tubes with EDTA additive for lab use
5. Yellow Top Tubes
- Additive: ACD or SPS
- Used For: DNA testing, cultures
Also Read : ACD Tubes: Uses, Types, Benefits, and Best Practices for Blood Collection
6. Grey Top Tubes
- Additive: Sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate
- Used For: Glucose testing
Need a visual aid? A phlebotomy tube color guide with chart can help you remember which tube to use for each test.
Phlebotomy Tubes Color Coding & Their Common Uses
| Tube Color | Additive | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Light Blue | Sodium Citrate | Coagulation Tests |
| Red | None or Clot Activator | Serum Tests, Drug Levels |
| Gold (SST) | Clot Activator + Gel | Chemistry Panels, Hormone & Vitamin Tests |
| Green | Heparin | Plasma Chemistries, ABGs |
| Lavender/Purple | EDTA | CBC, A1c, Hematology |
| Pink | EDTA | Blood Bank, Crossmatching |
| Gray | Oxalate + Fluoride | Glucose, Lactate, BAC |
| Royal Blue | EDTA/Heparin/None | Heavy Metals, Trace Elements, Micronutrients |
| Yellow | ACD/SPS | DNA Testing, Blood Cultures, Immunology |
Understanding the Order of Draw in Phlebotomy
Using phlebotomy tube in the correct sequence matters. The order of draw in phlebotomy tube collection procedure prevents cross-contamination between additives, which could affect test results.
Here’s the generally accepted order:
- Blood cultures (Yellow top – SPS)
- Coagulation tube (Light blue)
- Serum tubes (Red or Gold)
- Heparin tube (Green)
- EDTA tube (Lavender)
- Glycolytic inhibitor (Gray)
Not following the correct order of draw is one of the top mistakes phlebotomists make with blood tubes.
How to Avoid Common Mistakes
Even those who have been doing something for a long time might make blunders. Here are some things to be careful of:
1. Using the Wrong Type of Tube
Choosing the wrong tube might ruin the whole test.
2. Putting too much or too little in the tubes
The wrong amount might change the ratio of blood to additive.
3. Not Mixing Additives Right
To mix the additive, most tubes need to be turned upside down a few times just after they are collected.
4. Putting the wrong label on samples
To minimise misunderstanding and wrong diagnoses, always label and store phlebotomy tube correctly.
A Closer Look: Additives and What They Do
Different additives have different uses:
- EDTA (Lavender): Stops blood from clotting by binding to calcium, which is helpful for CBC testing.
- Sodium Citrate (Blue): Stops blood from clotting by binding calcium in a method that may be undone. This makes it perfect for coagulation.
- Heparin (Green): Stops thrombin and coagulation factors; utilised for plasma testing.
- Clot Activators (Red or Gold): These make the blood clot faster and are used for serum.
These capabilities of phlebotomy tube additives are very important for accurate lab testing.
Phlebotomy Tubes: Prons and Cons Glass vs. Plastic
Glass Tubes
- Pros: Chemically inert, high clarity
- Cons: Fragile, heavier
Plastic Tubes
- Pros: Shatter-resistant, safer for transport
- Cons: May have chemical leaching (modern plastics reduce this risk)
When choosing between the two, many professionals ask: glass vs plastic phlebotomy tubes – which to buy? For most clinical settings, plastic phlebotomy tubes for routine blood testing are preferred due to their durability and safety.
Best Practices for Handling and Storing Phlebotomy Tubes
- Store at room temperature
- Keep away from direct sunlight and moisture
- Always check expiration dates
- Use leak-proof blood collection tubes for transport to ensure sample safety
- Learn how to properly label and store phlebotomy tubes to reduce errors in identification
What to Look for When Buying Phlebotomy Tubes
Finding the correct tubes may affect both cost and performance, whether you’re a tiny clinic or a medical supply buyer. Here are some things to watch for:
1. Sterility and Shelf Life
Only purchase sterile vacuum phlebotomy tube from sellers you can trust. Check the expiry dates to prevent throwing away food.
2. Compatibility
Make sure the tubes function with either automated analysers or manual processing, depending on how you do things.
3. Tube Volume and Additive Type
Be aware of the exams you take most often. Depending on how many you need, get a number of phlebotomy tube with clot activator for blood tests or sodium citrate tubes for coagulation.
4. Storage and Shipping
Choose tubes that won’t leak and are strong, particularly if you’re sending samples or doing mobile phlebotomy.
Why Choose KDL Phlebotomy Tubes?
KDL is a trusted phlebotomy tube manufacturer and supplier, offering a full range of high-quality blood collection tubes designed for accuracy, safety, and compatibility with all major diagnostic systems. Our color-coded tubes—such as EDTA, Sodium Citrate, Heparin, and Clot Activator—are made with medical-grade additives and strict quality control to ensure precise results. Sterile, single-use, and CE/FDA certified, KDL phlebotomy tubes are the preferred choice for hospitals, clinics, and laboratories worldwide.
Final Thoughts
Phlebotomy tube may seem like a small component in the healthcare ecosystem, but their correct use has a huge impact on diagnostic accuracy. Whether you’re learning the order of draw in phlebotomy tube collection procedure, reviewing the phlebotomy tube color guide with chart, trying to avoid common errors when using blood collection tubes, or ready to buy phlebotomy tubes with EDTA additive for lab use, understanding the basics can go a long way.
Armed with this knowledge, you can make confident, informed choices about the products you use and how you use them—ensuring patient safety and lab accuracy every step of the way.
 +86-791-8686-1216
+86-791-8686-1216 

