
When doctors order a blood test, there’s more going on than just drawing a tube of blood. The way that blood is collected, stored, and processed can make a big difference in getting accurate results. One of the most important parts of this process in hematology is the use of EDTA blood tests.
EDTA may sound like a complicated chemical, but it plays a simple and vital role: it keeps the blood from clotting in the tube so that doctors and lab technicians can study it properly. Without it, many of the routine blood tests we rely on every day would not be possible.
In this post, we’ll break down what EDTA is, why EDTA blood tests are essential in hematology, and how they impact patient care.
Key Takeaways
- EDTA is an anticoagulant that prevents blood from clotting in collection tubes.
- EDTA blood tests are essential in hematology because they preserve cell shape and allow accurate counts.
- Most common blood tests, like the CBC, rely on EDTA tubes.
- EDTA is safe, effective, and widely used, but it isn’t suitable for every type of test.
- Doctors depend on EDTA blood samples to diagnose, monitor, and treat a wide range of conditions.
What Is EDTA?
EDTA stands for ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid—a mouthful, but it has a straightforward job. EDTA is a type of chemical called an anticoagulant. Anticoagulants stop blood from clotting outside the body.
When blood clots in a tube, it can no longer be used for many types of lab testing. That’s why EDTA is added to certain blood collection tubes, usually the purple-top tubes you may have seen in a lab or doctor’s office.
How EDTA Works
EDTA binds to calcium in the blood. Calcium is one of the key elements that allows blood to clot. By holding onto calcium, EDTA prevents the clotting process from happening. This makes sure the sample stays fluid and stable long enough for laboratory testing.
Why EDTA Blood Tests Matter in Hematology
Hematology is the branch of medicine that studies blood and blood-related disorders. To make accurate diagnoses, hematologists rely on blood that hasn’t clotted and still reflects the body’s natural state.
EDTA blood tests are the foundation for many of the most common hematology studies. Without EDTA, these tests wouldn’t be as reliable or accurate.
Common Hematology Tests That Use EDTA
Here are some examples of tests where EDTA blood Tube samples are essential:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): The most ordered blood test in medicine. It measures red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, hemoglobin, and hematocrit.
- Blood Smear Analysis: A microscopic look at the shape, size, and appearance of blood cells.
- Reticulocyte Count: Measures young red blood cells to see how well bone marrow is working.
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR): Checks inflammation in the body.
- Blood Parasite Testing: Detects parasites like malaria in blood cells.
Each of these tests provides crucial information about a patient’s health, and each one depends on the stability that EDTA provides.
The Role of EDTA in Accurate Blood Cell Counts
One of the most important things about EDTA blood tests in hematology is that they keep the shape of blood cells. Morphology is the study of how cells are shaped and built.
There will be no clear picture of what’s going on in the patient’s body if blood clots or cells break down in the tube. Because EDTA Tube helps keep blood cells whole, results are correct and useful.
Why the shape of cells is important
Red Blood Cells (RBCs): The size and form of red blood cells (RBCs) help doctors figure out if someone has anemia, sickle cell disease, or a vitamin deficiency.
White Blood Cells (WBCs): When white blood cells (WBCs) show up, it means you have an illness, a problem with your immune system, or even leukemia.
Platelets: Their count and shape can show clotting disorders or bleeding risks.
Without EDTA, these details might be lost, which could lead to the wrong diagnosis or failure to notice symptoms.
Also Read : A Complete Guide to K3 EDTA Tube
Benefits of Using EDTA Tubes in Hematology
The lavender or purple-top tubes, which are EDTA tubes, are widely used because they have several benefits:
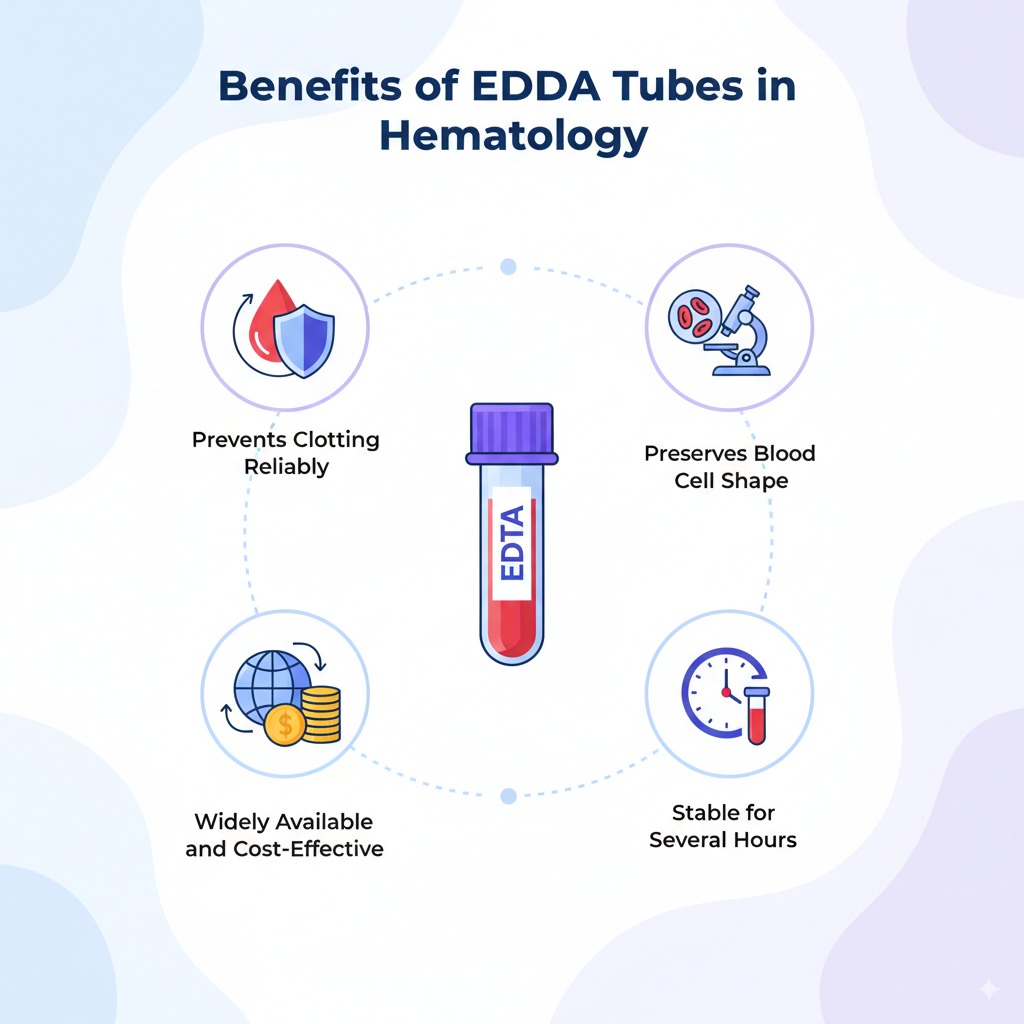
1. Prevents Clotting Reliably
When used properly, EDTA is a very good way to stop fluid from clotting. In many hematology tests, this makes it more accurate than other blood thinners.
2. Preserves Blood Cell Shape
While some other anticoagulants can damage or alter cells, EDTA does not when used correctly. Important for reliable imaging and computerized cell counts.
3. Widely Available and Cost-Effective
These EDTA tubes are cheap, simple to store, and widely used in hospitals and labs around the world.
4. Stable for Several Hours
Because blood in EDTA tubes can stay safe at room temperature for several hours, labs don’t have to rush through the process of processing samples.
Limitations of EDTA in Blood Testing
While EDTA blood tests are vital, they do have some limitations. It’s important to understand these to avoid errors.
Platelet Clumping
Sometimes, EDTA can cause platelets to clump together in rare cases. This can make platelet counts look falsely low. When this happens, doctors may order a different type of anticoagulant tube for repeat testing.
Not Suitable for All Tests
EDTA works great for hematology, but it’s not good for tests that measure minerals like calcium, potassium, or iron. Because EDTA binds to these minerals, it can interfere with results.
Also Read : A Complete Guide to K2 EDTA Tube
EDTA Compared to Other Anticoagulants
Labs utilize different anticoagulants based on the specific test requirements. Here’s a comparison of EDTA with other options:
EDTA and Heparin
- Heparin is frequently utilize in chemistry tests and blood gas analysis.
- EDTA is preferable for hematology as it preserves the integrity of cell shapes.
EDTA and Sodium Citrate
- Sodium citrate is primarily utilized in coagulation studies such as PT and aPTT.
- EDTA is the preferred anticoagulant for blood counts and morphology.
- This emphasizes the importance of selecting the appropriate anticoagulant for reliable test outcomes.
Why doctors use EDTA blood tests
EDTA blood tests are use in practically every patient’s treatment, from regular checks to critical diagnosis.
Monitoring Overall Health
CBCs are commonly done as part of yearly checkups to look for early indicators of anemia, infection, or blood abnormalities.
Diagnosing Illness
Hematologists use EDTA blood tests to detect illnesses including leukemia, malaria, and clotting abnormalities.
Guiding Treatment Plans
Doctors may choose the appropriate treatment, such as iron supplements, antibiotics, or chemotherapy, based on accurate blood test findings.
The Future of EDTA Blood Tests
Even as new technology changes the way blood is studied, EDTA will continue to play a key role. Automated machines, digital imaging, and advanced diagnostic tools still rely on high-quality samples—and that means EDTA will remain central in hematology.
Researchers are also exploring new additives and preservatives, but EDTA’s balance of effectiveness, safety, and cost makes it hard to replace.
Final Thoughts
Accuracy is the most important factor when it comes to blood testing. One of the unsung heroes of contemporary medicine is the EDTA blood test. They make sure that the findings physicians get are accurate and show what’s really going on in the body.
EDTA makes sure that hematology laboratories can execute their jobs with accuracy, from finding infections to diagnosing major blood illnesses. You could see the purple-top tube the next time you have your blood taken. Now you know how crucial it is.
 +86-791-8686-1216
+86-791-8686-1216 

