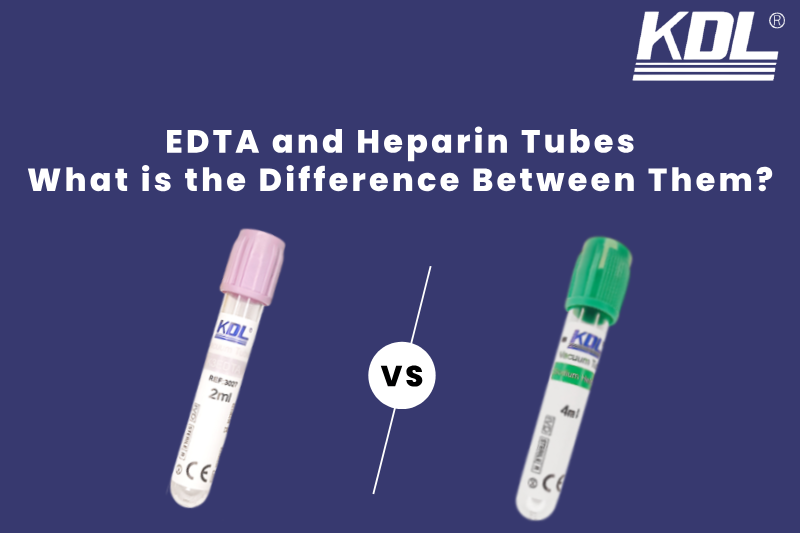
When you need blood tests at a clinic or hospital, you may notice that the nurse or phlebotomist draws your blood from different colored tubes.These tubes aren’t just for looks. Depending on what the lab needs to test, each one does a different job.Two of the most common are EDTA tubes and Heparin tubes.
If you’ve ever wondered, “What is the difference between EDTA and Heparin tubes?”.We’ll explain it in simple terms in this guide.We’ll talk about what they are, how they work, when to use each one, and why it’s important for getting correct lab results.
Why Do Blood Collection Tubes Have Additives?
Before we jump into EDTA and Heparin, let’s talk about why blood collection tubes have additives in the first place.
Quickly after leaving the body, blood starts to clot. In the lab, this can be a problem, but it’s good for treating wounds. Certain values, such as blood cell counts, may not always appear in clotted blood.
To prevent clotting, special chemicals called anticoagulants are added to some tubes. These chemicals keep the blood in liquid form long enough for labs to process it. Both EDTA and Heparin are anticoagulants, but they work in different ways.
What is an EDTA Tube?
EDTA stands for Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. It is a chemical that works by binding calcium in the blood. Since the body needs calcium for clotting, removing it prevents clots from forming.
Tube Color and Appearance
EDTA tubes are usually lavender (purple) or pink on the top. When you see a nurse pick up a purple top tube, it likely contains EDTA.
Common Uses of EDTA Tubes
EDTA tubes are use for:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) – a test that checks red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Blood films – for looking at blood cells under a microscope.
- Hemoglobin A1C – used in diabetes monitoring.
- Molecular tests – including some DNA and PCR studies.
Why EDTA Is Chosen
EDTA preserves the shape and size of blood cells better than most anticoagulants. This makes it very useful for hematology tests, where accurate cell counts are critical.
What is a Heparin Tube?
Heparin is a naturally occurring substance in the body. In tube form, it is made from animal tissues (usually pork or beef sources). It prevents clotting by enhancing the activity of antithrombin, a protein that blocks clotting enzymes.
Tube Color and Appearance
Heparin tubes are most often green-topped. Some may be light green or dark green, depending on the type of Heparin inside.
Common Uses of Heparin Tubes
- Chemistry panels:such as kidney function, liver function, and electrolyte testing.
- Determinations of plasma: when the laboratory requires plasma rapidly.
- Blood gases: determining the levels of pH, carbon dioxide, and oxygen.
- Certain specialized tests: like hormone levels or toxicology.
Why Heparin Is Chosen
Heparin works fast and doesn’t interfere much with most chemistry tests. Since it keeps plasma usable right away, labs often choose Heparin tubes for urgent testing.
Key Differences Between EDTA and Heparin Tubes
1. Anticoagulant Action
EDTA works by binding to calcium in the blood, which prevents clotting since calcium is essential for the process. Heparin operates in a different way, activating antithrombin, a naturally occurring protein in the body that inhibits clotting enzymes.
2. Tube Color
EDTA tubes are usually purple or pink on top, while Heparin tubes are green. These standard colors help nurses and lab staff quickly know which tube contains which additive.
3. Common Use
EDTA tubes are most often use for blood counts, like a CBC, because they keep blood cells looking normal. Heparin tubes are use for chemistry tests and blood gas studies because they make plasma ready for testing right away.
4. Sample Type
Blood collected in an EDTA tube is usually kept as whole blood or sometimes used for plasma. Blood in a Heparin tube is mainly use to separate plasma, which is needed for many chemistry tests.
5. Stability of Samples
It’s important to know that EDTA can keep blood cells in their usual shape for hours, which is useful for cell counts. In addition, heparin excels at maintaining steady chemical levels in plasma, ensuring accurate detection.
6. Speed of Action
While EDTA stops blood from clotting pretty fast, Heparin does so almost instantly. This is why medical professionals frequently use it in emergency or STAT tests.
7. Preservation of Blood Cells
EDTA is great at keeping red and white blood cells whole, which lets labs count them correctly. So it’s not the best choice for hematology tests because it doesn’t keep blood cells as well.
8. Shelf Life of Sample
If stored correctly, blood can remain viable for hematology tests for an extended period, sometimes up to 24 hours. If you want accurate chemistry data, you should use heparinized plasma as soon as possible, usually within a few hours.
Quick comparison of EDTA and Heparin tubes for easy reference:
| Feature | EDTA Tube (Purple/Pink) | Heparin Tube (Green) |
|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulant Action | Binds calcium to prevent clotting | Activates antithrombin to block clotting enzymes |
| Common Use | Blood counts (CBC), keeps blood cells normal | Chemistry tests, blood gas studies, plasma testing |
| Sample Type | Whole blood or sometimes plasma | Mainly plasma for chemistry tests |
| Stability of Samples | Preserves blood cell shape for hours | Keeps plasma chemical levels stable for accurate testing |
| Speed of Action | Stops clotting fairly fast | Stops clotting almost instantly; ideal for emergency tests |
| Preservation of Blood Cells | Excellent, keeps red and white cells intact | Not as effective for blood cells; not ideal for hematology |
| Shelf Life of Sample | Usable for hematology tests up to 24 hours | Best used within a few hours for accurate chemistry results |
EDTA and Heparin Tubes: Why Choosing the Right Tube Matters
Using the wrong blood tube can completely change test results. For example:
- If an EDTA tube is used instead of a Heparin tube for a chemistry test, the calcium result will look extremely low. This isn’t because the patient has low calcium, but because EDTA bound it all up.
- If a Heparin tube is used for a CBC, white blood cells might clump together, making the results unreliable.
This is why nurses, phlebotomists, and lab technicians follow a strict order of draw and use specific tubes for each test.
Order of Draw: Where Do EDTA and Heparin Tubes Fit?
When multiple blood samples are collected, there is a recommended sequence called the order of draw. This prevents additives from one tube from contaminating another.
The usual order is:
- Blood culture bottles
- Coagulation tubes (light blue top)
- Serum tubes (red, gold, or tiger top)
- Heparin tubes (green top)
- EDTA tubes (purple or pink top)
- Other tubes (gray, yellow, etc.)
Why Choose KDLNC EDTA & Heparin Tubes?
At KDLNC, we know that accurate lab results start with reliable blood collection. That’s why our EDTA and Heparin tubes are carefully design to support precision diagnostics with:
- High-quality anticoagulants to ensure consistent clot prevention for hematology and chemistry testing.
- Sterile, leak-proof tubes to protect both samples and healthcare staff during collection and transport.
- International quality certifications with full documentation available to meet global laboratory standards.
- Optimized shelf life to maintain sample stability and accurate results across a wide range of applications.
With certified manufacturing standards and stringent quality checks, KDLNC ensures every EDTA and Heparin tube delivers dependable performance for modern laboratories.
Final Thoughts
In the end, EDTA and Heparin tubes may just look like colorful containers, but they each have a very important job. EDTA tubes, with their purple or pink tops, are best for counting and studying blood cells. Green tubes called heparin are use for chemistry tests and to check plasma. When doctors use the right tube, they can get accurate data that help them make the best health decisions for you. When you see a blood draw again, you’ll know that each tube was picked with great care and that each color is used for a specific reason.
Key Takeways
- EDTA (purple/pink): For blood counts and hematology; binds calcium to prevent clotting; preserves blood cell shape.
- Heparin (green): For chemistry tests and plasma analysis; blocks clotting enzymes; preserves plasma components.
- Sample type: EDTA gives whole blood or plasma for cell studies; Heparin gives plasma for chemical tests.
- Accuracy: Using the wrong tube can give false results, like abnormal calcium or potassium levels.
- Speed: Heparin works fast, ideal for urgent tests; EDTA is best for detailed blood cell analysis.
- Common tests: EDTA for CBC, hemoglobin, blood films; Heparin for liver/kidney panels, electrolytes, and blood gases.
 +86-791-8686-1216
+86-791-8686-1216 

