If you work in the medical field or you’re training to become a healthcare professional, you’ve probably heard the term “blood glucose tube.” But what exactly is it? How is it use? And why is it so important in healthcare settings?
This complete guide will walk you through everything you need to know about blood glucose tubes—from what they are and how they work, to how you can buy the best ones for your practice.
Whether you’re a nurse, lab tech, doctor, or medical student, this post will help you understand the basics while also giving tips for choosing quality glucose tubes for blood collection.
What Is a Blood Glucose Tube?
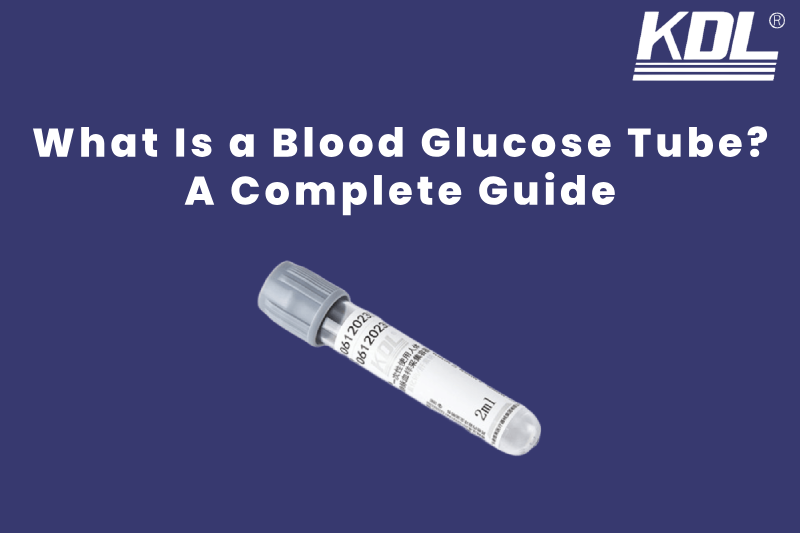
A blood glucose tube is a special type of blood collection tube use to test glucose (sugar) levels in a patient’s blood. These tubes are a part of vacutainer blood collection systems, which is use to draw and store blood samples for lab testing.
Blood glucose tubes usually contain a special chemical (call an additive) that helps stop the blood from changing before it’s tested. This additive prevents the red blood cells from using up the glucose in the blood sample. This keeps the glucose level accurate for testing.
Blood Glucose Tube Color Code
In most clinical labs, color-coding helps quickly identify different types of tubes. For glucose testing, the gray-top tube is standard.
| Tube Cap Color | Additive | Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Gray | Sodium Fluoride + Potassium Oxalate | Glucose testing, blood sugar monitoring |
Other tube colors is use for different tests (e.g., red for serum, purple for hematology), but for glucose, gray is the go-to.
Why Are Glucose Tubes Important?
Glucose levels are an important indicator for many health conditions. Some of the most common reasons for glucose testing include:
- Diabetes screening and monitoring
- Checking for hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
- Diagnosing metabolic disorders
- Monitoring patients with insulin treatment
Using the correct glucose collection tube is crucial. If the wrong tube is use, or if there is no additive to stop glucose breakdown, the test results might be incorrect. This can lead to the wrong diagnosis or treatment.
What is Inside a Blood Glucose Tube?
The key ingredient inside a blood glucose tube is an additive. There are two common types:
- Sodium Fluoride (NaF) – This additive prevents glycolysis, which is the process where blood cells use glucose.
- Potassium Oxalate (KOx) – This works as an anticoagulant, meaning it stops the blood from clotting.
Most glucose tubes for blood tests contain both sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate. These are often called gray-top tubes because the tube cap is usually gray.
How Is a Glucose Tube Used?
Using a glucose collection tube is simple for trained professionals. Here’s a quick overview of the process:
- Prepare the patient – Make sure the patient is sitting or lying down.
- Disinfect the site – Clean the area where the blood will be drawn.
- Draw the blood – Use a vacutainer needle and holder to collect the blood.
- Fill the tube – The blood flows into the gray-top tube automatically.
- Invert the tube – Gently turn the tube up and down about 8–10 times to mix the additive with the blood.
- Label the tube – Write the patient’s name, date, and time.
This helps ensure accurate results when the sample is test in the lab.
When to Use a Blood glucose Test Tube
Diabetes tubes are use for a number of different tests by medical workers. In the following cases,
- Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) Test: Checks how much glucose a person has after 8 to 12 hours of not eating.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): If you drink a glucose solution and then take the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), it checks how well your body handles sugar.
- Random Blood Sugar Test: This test can be done at any time of the day, even after a meal.
- The postprandial glucose test: It is done two hours after a meal to see how the food changed the blood sugar level.
These tests help find and treat metabolic diseases like type 1 and type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and others.
Storage and Handling of Glucose Tubes
To keep the blood sugar tubes working properly:
- Store at room temperature – Keep tubes in a dry, cool area.
- Check expiration dates – Don’t use expired tubes, as the additives may not work well.
- Avoid freezing – Extreme cold can affect the chemical inside.
Always follow your lab or hospital’s guidelines for storing and handling collection tubes.
Things to Think About When Buying Blood Glucose Tubes
If you run a clinic, hospital, or lab and want to buy a lot of blood glucose tubes, here are some things to think about:
1. Quality of the Tube
Buy tubes from medical providers you can trust. Tubes that are cheap or of poor quality might cause leaks, clots, or wrong findings.
2. Size of the Tube
Most tubes hold a specified amount, such as 2 mL, 3 mL, or 5 mL. Choose the size that works for your tests.
3. Sterility
Check that the glucose tubes are clean and sealed well.
4. Type of Additive
Check that the tubes include sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate if you need full glucose preservation.
Conclusion: Why Glucose Tubes Matter in Everyday Medical Practice
Blood glucose tubes are a small but important part of taking care of patients every day. They make it easier and safer for doctors to keep an eye on and treat conditions like diabetes.
By using the right glucose collection tubes, doctors can be sure that the test results are accurate and that the care they give to patients is based on correct information.
It can be very helpful to know how glucose tubes for blood sugar testing work when you’re learning how to draw blood, training new staff, or just looking to stock up for your lab.
Shop High-Quality Blood Glucose Tubes Today
Looking to buy blood glucose tubes in bulk or need a reliable supply for your clinic? Check out our specimen collection product catalog or shop gray-top glucose tubes for the best prices and fast shipping.
 +86-791-8686-1216
+86-791-8686-1216 

