Getting accurate blood tests begins long before the sample gets to the lab. The kind of tube used to collect the blood is one of the most important things to do shortly after the blood is extracted to make sure the test findings are accurate. Enter serum blood collection tubes. These basic but important instruments are very important for clinical diagnostics because they assist laboratories separate serum from whole blood so that they can analyze it correctly.
This article will explain all you need to know about serum collection tubes, whether you work in healthcare, are a medical student, or are simply interested in how blood tests operate. We’ll talk about what they are, how they operate, different kinds, color codes, additives, and why they are important.
What Is a Serum Collection Tube?
A serum collection tube is a specialized blood collection container used in venipuncture to collect and store blood samples specifically for serum analysis. These tubes allow blood to clot, separating the serum from the blood cells and clotting factors during centrifugation.
Serum is the clear, yellowish fluid that remains after blood has clotted and the cells and clotting proteins are removed. It contains electrolytes, hormones, antigens, antibodies, and other analytes used in a wide range of diagnostic tests — from metabolic panels to hormone levels.
Benefits of Serum Collection Tubes
Serum collection tubes are a staple in medical labs for good reason. They make the process of collecting and testing blood samples more accurate, efficient, and safe — for both patients and healthcare professionals. Here are some of the key advantages they offer:
1. Clear, Accurate Results
Serum doesn’t contain blood cells or clotting proteins, which means it provides a clean sample for testing. This helps labs get more accurate readings, especially for things like hormone levels, liver enzymes, and antibodies.
2. Stable Samples
Once separated, serum holds up well. It stays stable longer than whole blood, which is important when samples need to be transported, stored overnight, or shipped to off-site labs.
3. Easy Separation with Gel Tubes
Some serum tubes come with a gel barrier that forms during centrifugation. This gel sits between the serum and the clot, making it easier to separate the serum without contamination or mixing — a big help in busy lab settings.
4. Used in a Wide Range of Tests
Serum is the go-to for many routine and specialized blood tests, including:
- Metabolic panels
- Liver and kidney function tests
- Vitamin and mineral levels
- Hormone testing
- Infectious disease screening
Because it’s used in so many types of testing, blood collection tubes for clinical diagnostics are one of the most versatile tools in lab work.
5. Faster Turnaround in Urgent Situations
In emergency cases, orange-top tubes — which help the blood clot quickly — allow labs to process and test the sample in just a few minutes. This is especially helpful in hospitals and ERs where every minute counts.
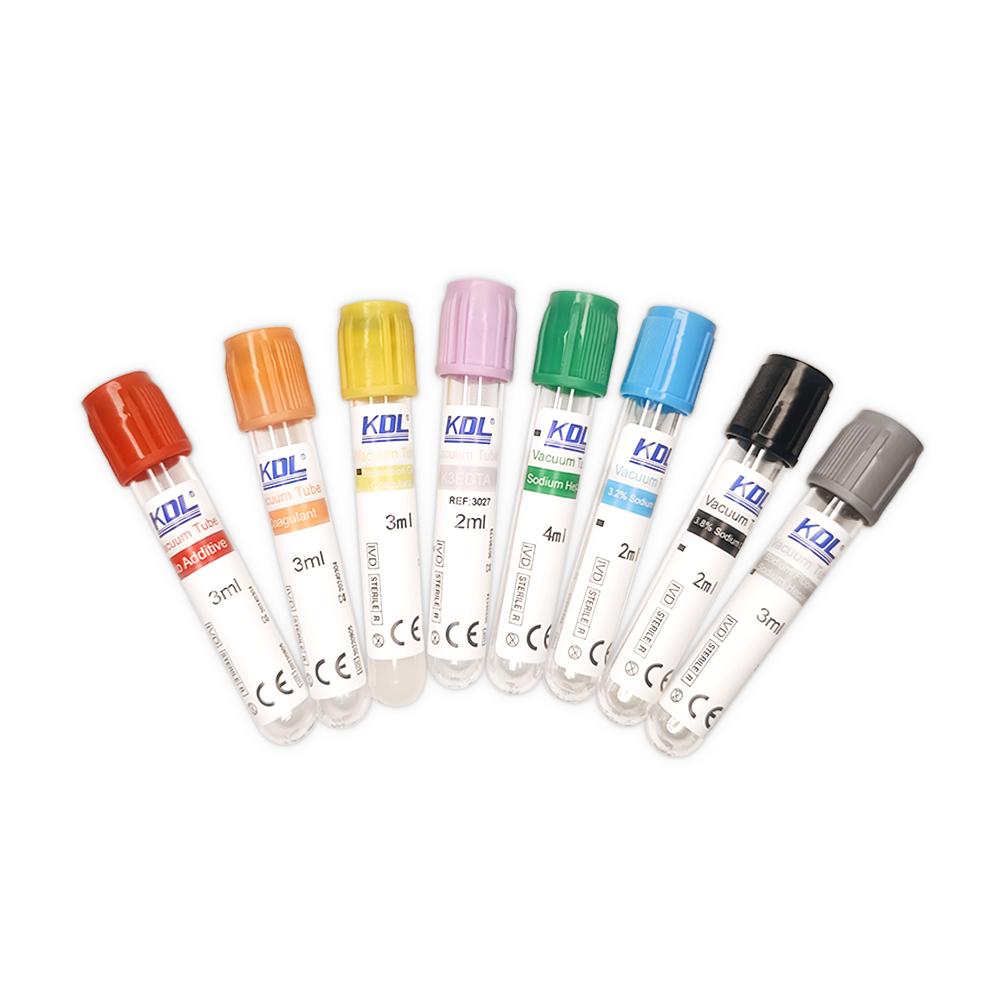
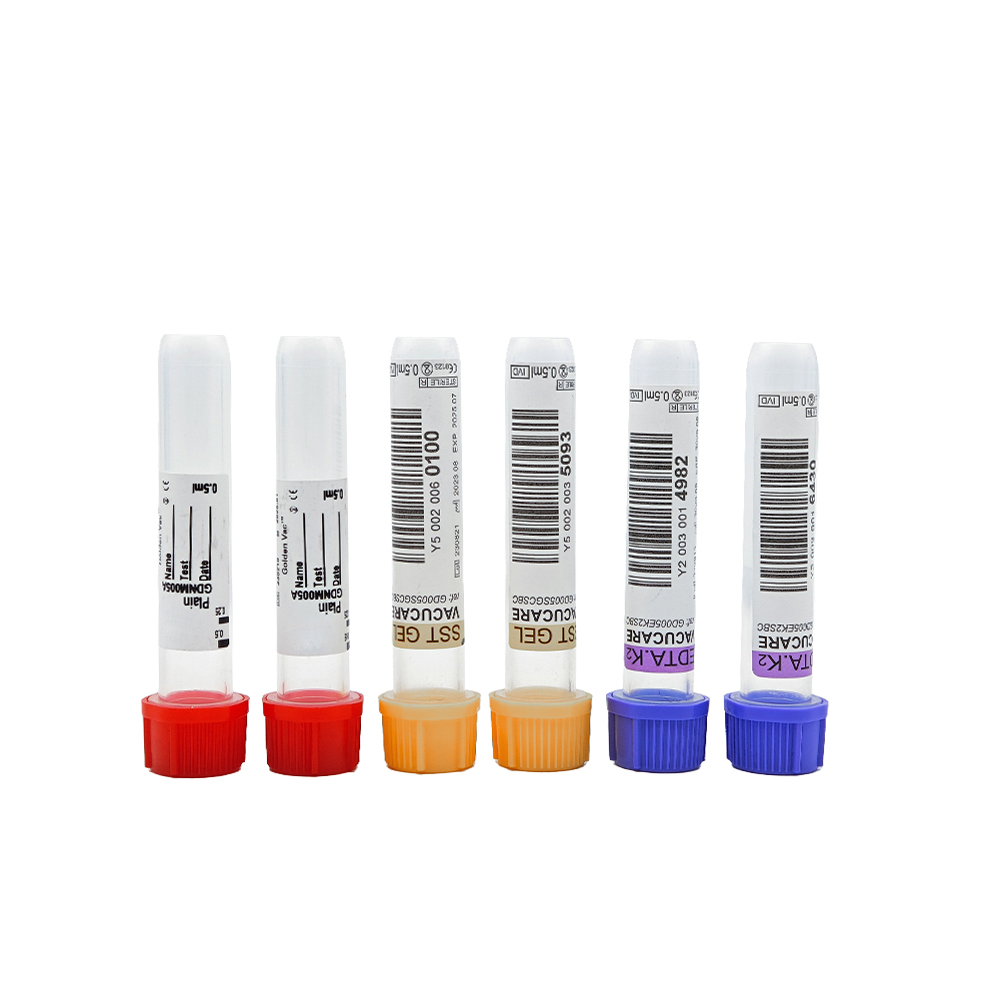
6. Color-Coded for Safety
Serum tubes are easy to recognize thanks to their color coding — usually red, gold, or orange. This helps nurses, phlebotomists, and lab techs grab the right tube for the right test, cutting down on mistakes.
7. Cleaner Samples, Fewer Problems
When drawn and handled properly, serum tubes help reduce the chance of hemolysis — a breakdown of red blood cells that can mess with test results. They also avoid the chemical interference that some anticoagulants can cause.
Why Is Serum Important in Blood Testing?
Many lab procedures use serum because it is a clean, cell-free sample that makes it easier to analyze certain analytes. Serum is thought to be more reliable for many biochemical tests than plasma, which has clotting factors in it.
Some of the most frequent tests done on serum are:
- Liver function tests (LFTs)
- Kidney function tests
- Hormonal assays (like TSH or testosterone)
- Infectious disease serology
- Nutrient level assessments (vitamins, minerals)
Using the right type of blood collection tube ensures that the findings are proper and free of contamination, which is important for patient care.
Types of Serum Collection Tubes
There are different types of serum tubes, and they can vary based on additives, color codes, and intended use. Here’s a breakdown of the most commonly used types.
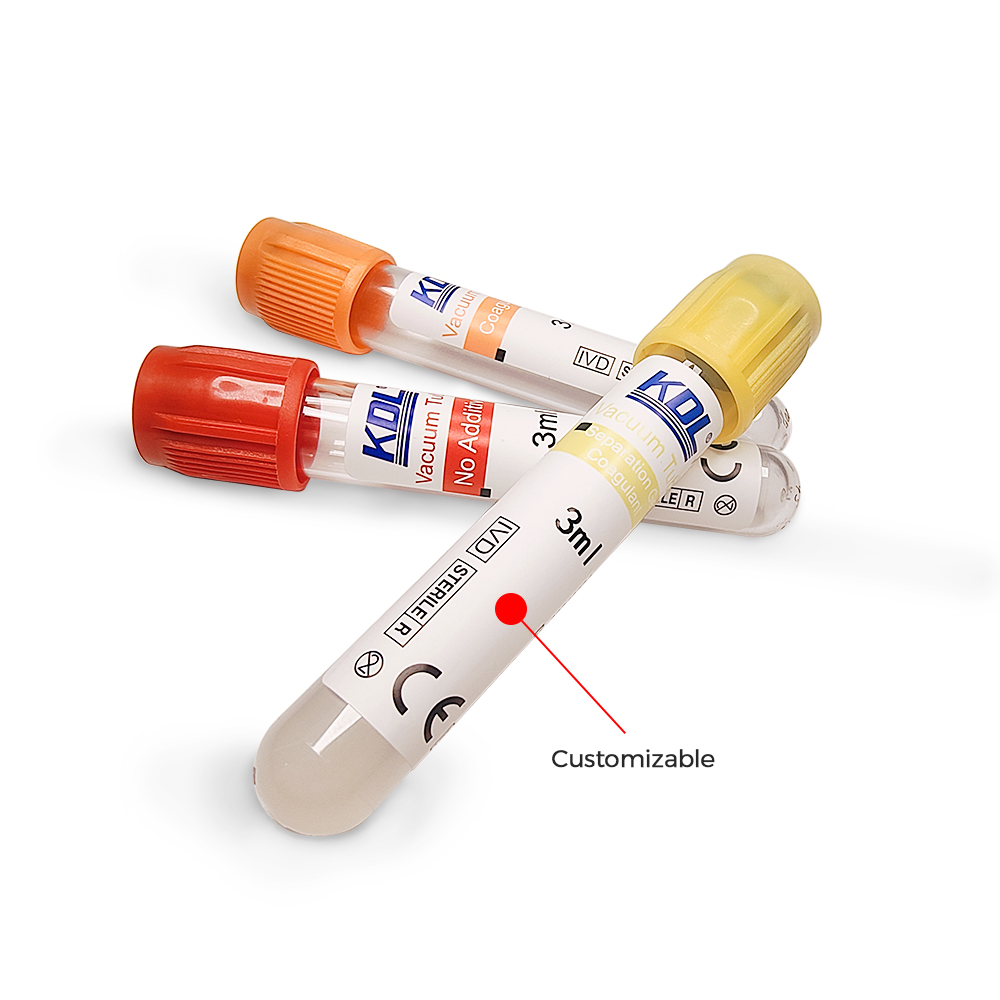
1. Red-Top Tubes (Plain Serum Tubes)
- Additive: No anticoagulant; no gel
- Used For: Chemistry, serology, and immunology tests
- Clotting Time: 30–60 minutes at room temperature
Red-top tubes are the most basic serum collection tubes. They contain no anticoagulants or gel barriers, which means after centrifugation, the serum must be carefully pipetted out.
2. Gold-Top Tubes (SST Tubes – Serum Separator Tubes)
- Additive: Clot activator and gel separator
- Used For: Routine chemistry, endocrine, and serology tests
- Clotting Time: 30 minutes
Gold-top or SST (Serum Separator Tubes) are among the most widely used serum tubes in clinical labs. The gel barrier settles between the serum and the clot after centrifugation, allowing for easy and contamination-free serum retrieval.
Also Read : How to Choose the Right Serum Separator Tube for Your Lab
3. Orange-Top Tubes (Rapid Serum Tubes)
- Additive: Thrombin-based clot activator
- Used For: Emergency labs, STAT testing
- Clotting Time: 5 minutes
These are designed for rapid clotting, perfect in urgent care procedure or when a fast turnaround is essential.
Important Things to Think About When Using Serum Tubes
It’s very important to handle serum collecting tubes correctly. Here are some good ways to do things:
1. Gently Invert the Tube
After you collect the sample, turn the tube upside down five to eight times (don’t shake it) to mix the clot activator well. This makes sure that the clotting is even.
2. Allow Full Clotting Before Centrifugation
Before spinning, give the sample the right amount of time to clot. Centrifuging too soon may cause the clot to not fully form, which can leave fibrin strands in the serum.
3. Maintain and transport at the right temperatures
Follow the lab’s rules on how to store samples. If you don’t analyze serum samples within a few hours, you should put them in the fridge.
Final Thoughts
Serum collection tubes are more than simply devices for the lab; they are important for getting the right diagnosis and caring for patients. Knowing how they function, when to use them, and how to correctly employ them may really improve the quality and dependability of tests.
Whether you’re drawing blood in a busy clinic, preparing samples in a lab, or studying for your phlebotomy certification, understanding how serum tubes work can help you make sure that the lab findings are always correct and of high quality.
 +86-791-8686-1216
+86-791-8686-1216